Artificial intelligence is increasingly reshaping how work is performed across the United States, raising urgent questions about whether AI is replacing jobs and at what scale. While headlines often predict widespread unemployment, the actual data for 2024 and 2025 paint a more nuanced picture.
This research-based analysis examines the most credible AI replacing jobs statistics in the U.S., separating measured job losses from task automation, and comparing them against AI-driven job creation. Using verified data from labor reports, enterprise surveys, and economic research, this article provides a clear, up-to-date view of how AI is impacting employment today and what the evidence suggests for 2025.
10 most interesting AI replacing jobs statistics
- AI can technically perform work equal to ~11.7% of U.S. jobs (capability/exposure estimate, not confirmed layoffs).
- ~55,000 jobs were linked to AI-related cuts through 2025, and over 75% of those occurred after 2023.
- ~119,900 AI-related roles were added in 2024, which exceeds confirmed AI-linked losses.
- 51% of American workers worry AI will replace their jobs by 2026.
- 66% of enterprises are reducing entry-level hiring due to AI (a pipeline shock that can hit new grads hardest).
- 91% of enterprises report roles have changed or been eliminated by automation (job redesign is happening at scale, even when layoffs look “small”).
- In some data-heavy industries, AI adoption rates reach ~60–70%, increasing automation pressure on routine tasks.
- Software developers are projected to grow 17.9% through 2033 (a counterintuitive “AI won’t kill all dev jobs” signal).
- Employment in high AI-exposure jobs fell ~13% for workers aged 22–25 (early-career impact signal).
- AI skills command a ~56% wage premium compared to comparable non-AI roles (winner-takes-more dynamic).
Defining AI job replacement
Most AI adoption reshapes how jobs function. Entire positions rarely disappear overnight. Understanding this difference helps explain the gap between fear and data.
Key distinctions
- Task automation means AI handles parts of a job.
- Full job elimination happens far less often.
- MIT research estimates AI can handle work equal to 11.7% of U.S. jobs.
- That estimate reflects technical capability, not real job cuts.
10+ AI replacing jobs statistics in the U.S. (2024-2025)
Displacement exists but remains limited in scale. Hiring linked to AI tools, systems, and oversight continues to offset losses.
Recorded AI-related layoffs
About 55,000 jobs were linked to AI-related cuts through 2025. Over 75% of these occurred after 2023. These cuts still represent a small share of overall labor turnover.
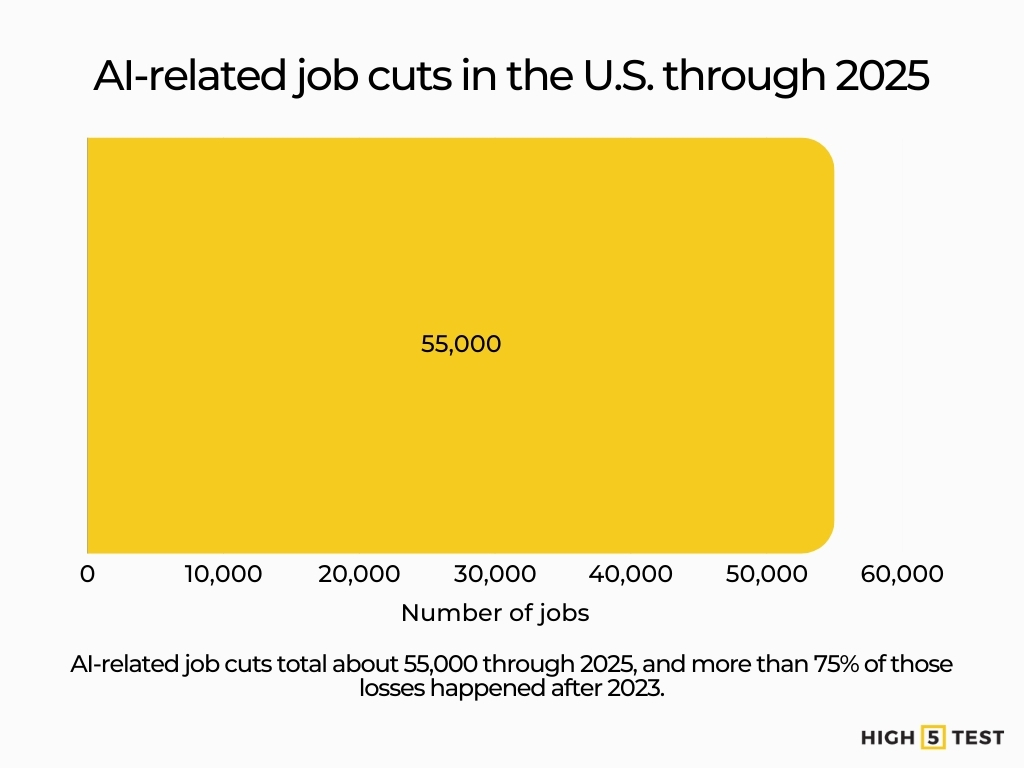
Source: Fortune
AI-driven job creation
Roughly 119,900 AI-related roles were added in 2024. This total far exceeds confirmed AI-driven job losses.
Source: Information Technology & Innovation Foundation
Employment statistics influenced by AI automation
51% of American workers worry about AI replacing their jobs by 2026.
Source: Resume Now
Surveys indicate that 66% of enterprises are reducing entry-level hiring due to AI, and 91% report that roles have changed or been eliminated by automation.
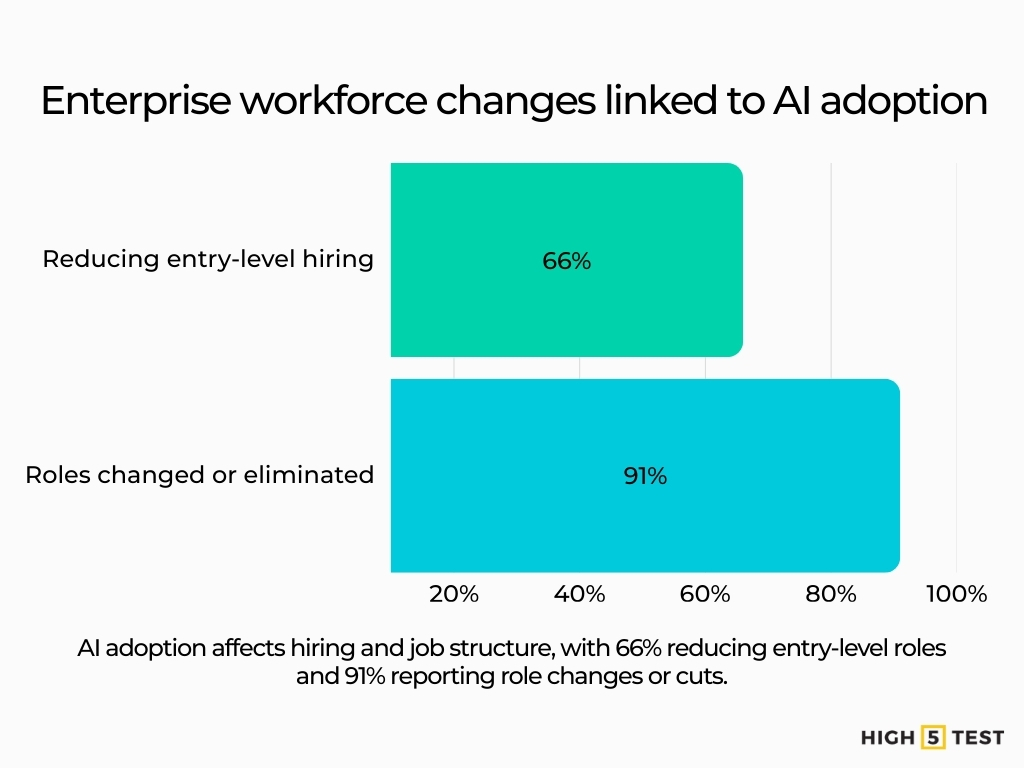
Source: IT Pro
Employers adjust hiring before cutting staff. Entry-level positions feel the impact first. Changes in job structure matter more than headline layoffs.
Data on fields with high AI adoption
AI impact varies by industry. Task type matters more than job title. Growth remains strong in roles tied to judgment, care, and advanced technical skills.
Most affected sectors
Industries with strong data can have AI adoption rates of 60-70%, making associated jobs more vulnerable to automation. Entry-level and routine tasks face a higher risk of displacement due to automation tools.
Source: World Economic Forum
Sectors with lower risk or growth
Healthcare and technical occupations (e.g., software developers projected to grow 17.9% through 2033) are less likely to disappear.
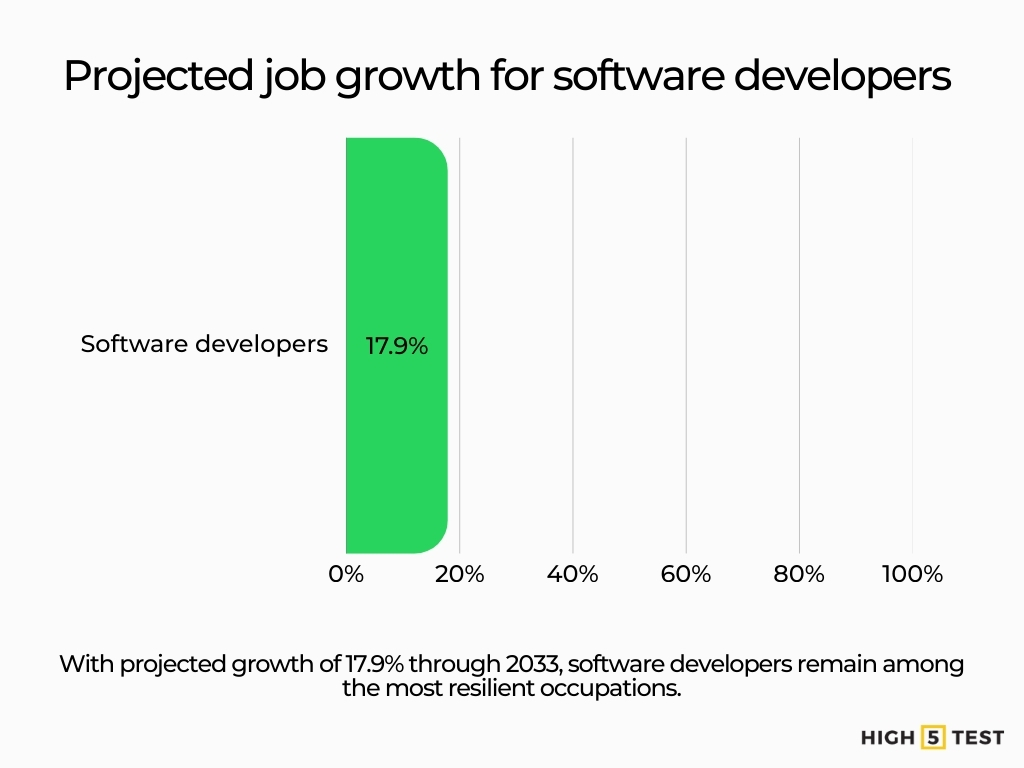
Source: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics
Statistics on workforce segments with greater AI exposure
Employment in high AI-exposure jobs fell by about 13% for workers aged 22 to 25. Employment rose among older workers in the same fields. Non-routine and high-skill jobs show lower exposure.
Source: Stanford University
Younger workers often hold entry-level positions with repetitive tasks. Older workers benefit from experience and task variety that AI handles less well.
Net jobs statistics: Gains vs. losses
Job creation and growth
AI skills command a ~56% wage premium compared to non-AI jobs.
Source: PwC
Some estimates suggest AI could generate ~170 million new jobs globally, outweighing elimination estimates.
Source: World Economic Forum
Job displacement estimates
Global models predict up to ~92 million jobs may be eliminated by AI, though these figures include global and not U.S-specific roles.
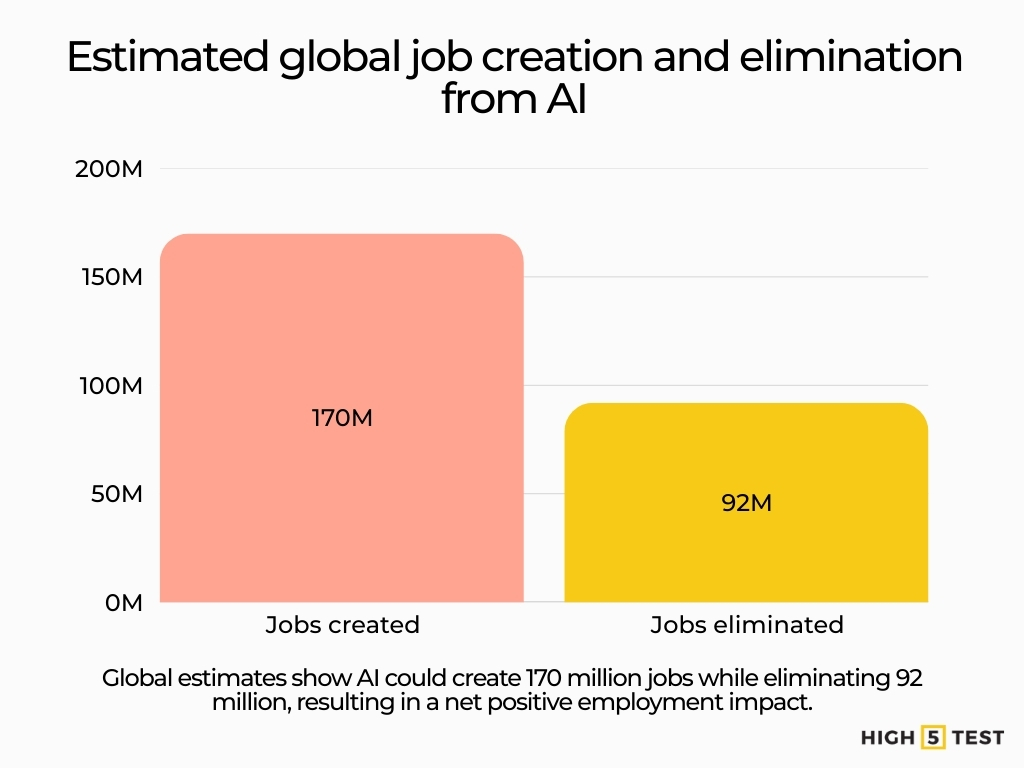
Source: World Economic Forum
Data on economic output in AI-exposed industries
Industries with high AI exposure saw revenue per employee grow by about 27% from 2018 to 2024. Less exposed industries grew by about 9%.
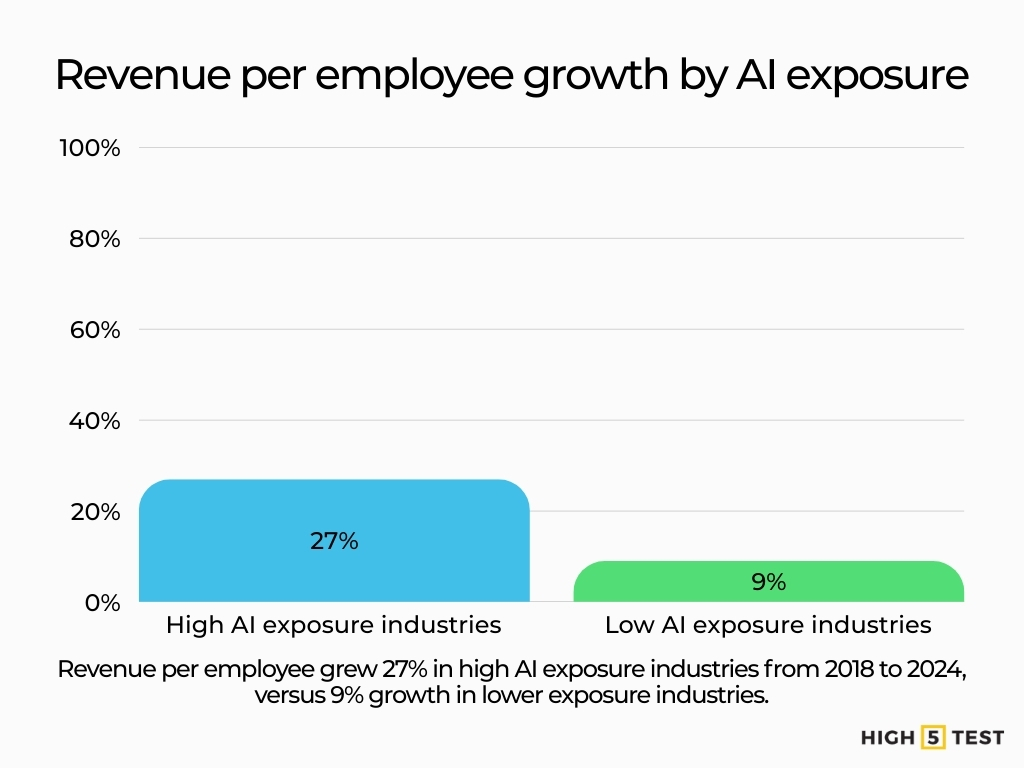
Source: PwC
Productivity gains help explain continued hiring. Companies invest in AI to expand output, not only to cut costs.
Conclusion
U.S. employment data from 2024 and early 2025 shows that AI is reshaping work faster than it removes jobs. Hiring tied to AI continues to exceed displacement. Task automation drives most change, not full job elimination.
Public concern about job loss is real. Evidence of large-scale displacement remains limited. Employers and policymakers focus on retraining, education, and AI oversight rather than banning automation. AI changes how work happens. It does not signal the end of work itself.
FAQ
How many U.S. jobs will AI replace by 2030?
Current projections estimate that about 6.1% of U.S. jobs could be lost by 2030 due to AI and automation. This figure reflects long-term structural change rather than immediate layoffs. Most impact is expected to come from gradual task replacement and job redesign instead of sudden job removal.
Is AI creating more jobs than it eliminates?
Yes. In 2024, AI-related hiring reached about 119,900 jobs. Confirmed AI-driven losses were about 12,700.
What percent of workers fear job replacement by AI?
Approximately 30% of U.S. workers report fearing AI could replace their jobs.
