The U.S. hiring landscape in 2024-2025 has been transformed by increased applicant volumes, widespread adoption of AI/ATS tools, and growing concerns about fairness and transparency. Employers are under pressure to process resumes more efficiently while maintaining quality, relevance, and diversity in hiring outcomes. This report section examines evidence from U.S. and international academic/industry studies on how AI is being used in recruitment: its impact on time savings, employer perceptions, HR practices, and the trade-offs in fairness and bias.
10 most interesting resume statistics
- ~180 applicants per hire in U.S. SMBs (2024, all industries).
- U.S. Applicant → Interview conversion ≈ 5%, Interview → Hire about 36%.
- Applications-per-hire up ~182% since 2021 in U.S. ATS data (Q4 2023–Q3 2024).
- Age discrimination/barrier perception: 64% of U.S. workers aged 50+ have seen or experienced age discrimination; 74% believe age will be a barrier to hiring.
- Systemic bias in race & gender via AI screening documented by Brookings and UW: notable disparities in how names/identities impact screening outcomes.
- 6-8 seconds average first glance duration on a resume; similarly, 6-7 seconds on average.
- 57% of hiring managers spend 1-3 minutes reviewing promising resumes; 21% spend over 3 minutes; only ~22% spend less than 1 minute.
- 73% of hiring managers reject candidates due to poor formatting of resumes.
- 153.77 applicants per job ad in San Jose, CA (1-week window, LinkedIn).
- Dubai leads globally with 285.21 applicants per LinkedIn ad (1 week).
50+ resume statistics and metrics (U.S., 2024–2025)
Average resumes per job posting (U.S.)
U.S. SMB benchmark: ~180 applicants per hire in 2024 (all industries). This reflects the average application volume per completed hire across U.S. SMBs.
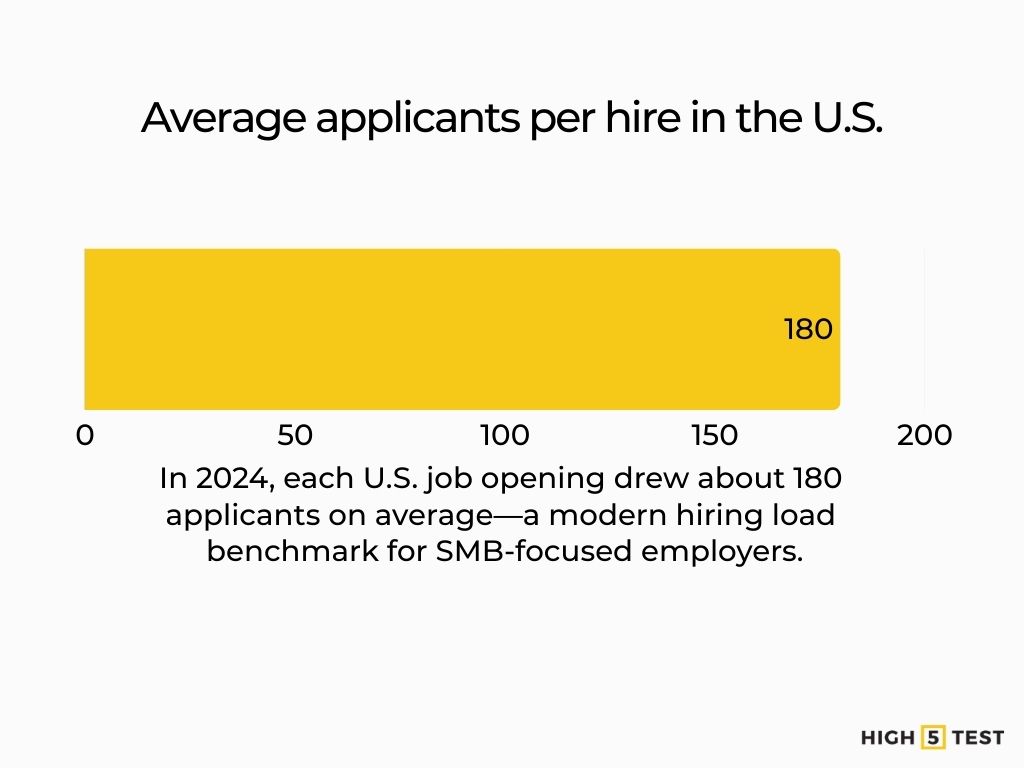
Source: CareerPlug
City-level (LinkedIn, 1-week window): San Jose, CA averages 153.77 applicants per job ad in a week, the highest among U.S. cities analyzed—illustrating elevated competition in tech hubs.
Source: Resume.io
Global comparisons
Dubai leads globally with an average of 285.21 applicants per LinkedIn ad (1 week), outpacing major U.S. markets.
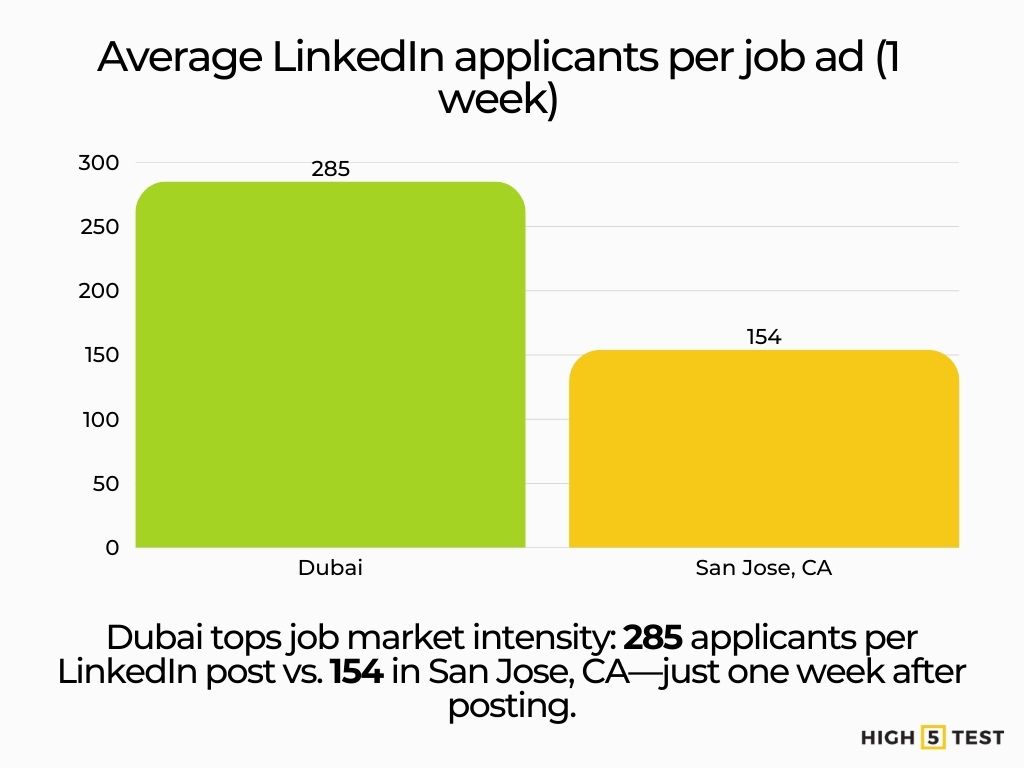
Source: Resume.io
United Kingdom (cross-market signal): UK platforms recorded ~48.7 applications per vacancy in Nov 2024, reflecting a sharp YoY rise and intense competition.
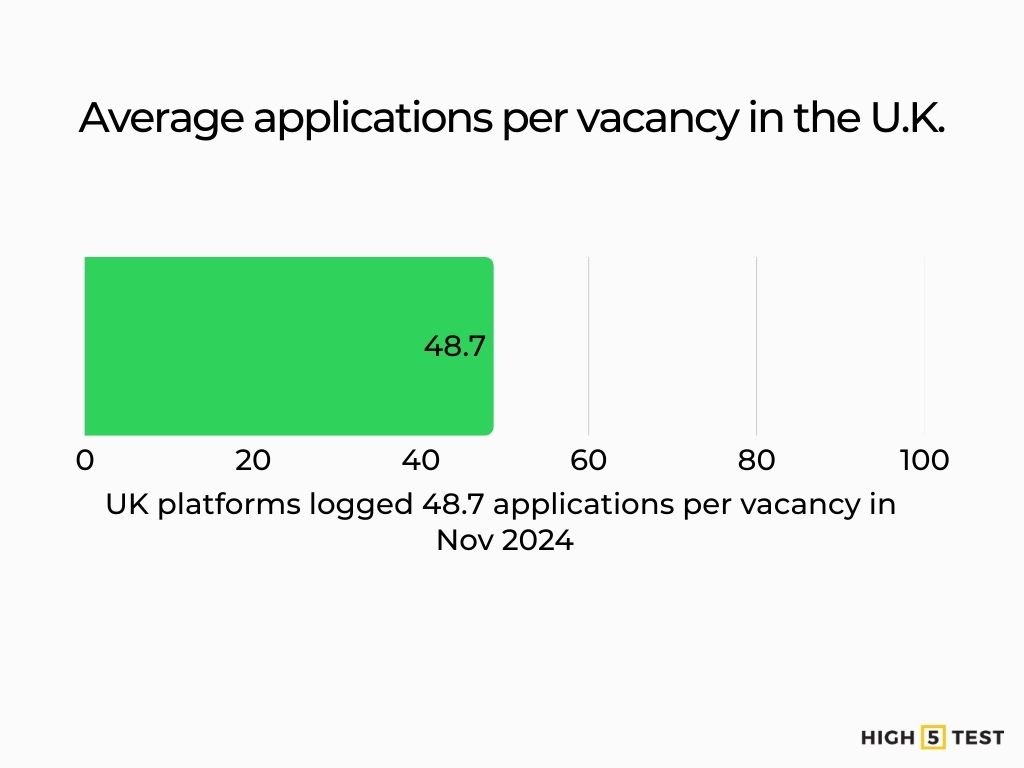
Source: TribePad
Interview conversion rate (U.S.)
Applicant → Interview: 5% (average across industries, U.S. SMBs). In other words, about 1 in 20 applicants reach an interview.
Interview → Hire: 36% on average—once candidates reach interviews, over a third convert to offers/hire in SMB benchmarks.
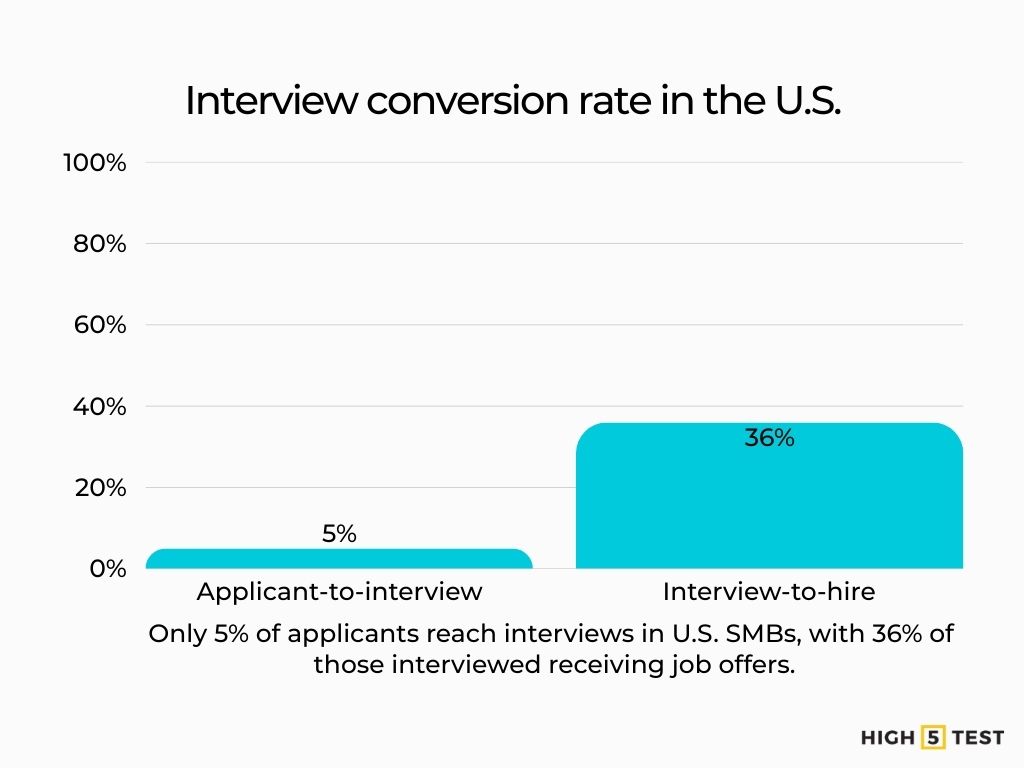
Source: CareerPlug
Context and comps
These pass-through rates help explain why job seekers must apply widely and target their materials; even modest gains in Applicant→Interview can meaningfully improve outcomes.
Application volume per job
U.S. applications per hire are up ~182% since 2021, based on a multi-year ATS analysis (Q4’23–Q3’24), confirming a structural jump in application density per filled role.
Source: Ashby
Implication: Screening loads are materially higher than pre-2021 norms; employers increasingly rely on ATS/AI and structured criteria, while candidates face greater competition per opening.
Source: Ashby
Global signals
The UK saw elevated applications per vacancy through late-2024 (≈48.7 per job in Nov), aligning with the global pattern of rising applicant-to-vacancy ratios.
Source: TribePad
Demographic breakdown highlights
Age (50+): Research reports 64% of U.S. workers 50+ have seen/experienced age discrimination, and 74% believe age will be a barrier to hiring, factors that influence resume strategy (like recency-focused content, skills emphasis).
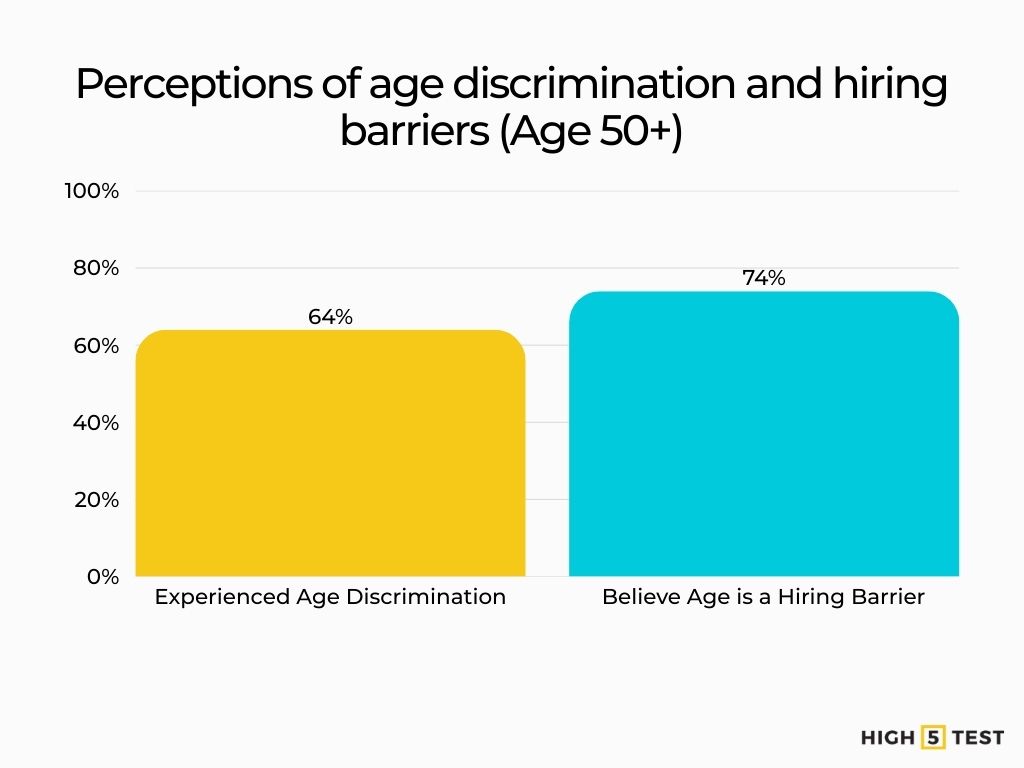
Source: AARP
Race and gender (AI screening): Analyses show systemic bias risks in AI resume-screening tools by race and gender, reinforcing the need for human oversight and bias audits.
Source: Brookings, University of Washington Information School
Experimental evidence (callbacks): Large-scale U.S. resume experiments continue to find racial disparities in employer responses—an external factor affecting resume outcomes beyond content quality.
Source: UC Berkeley
How recruiters read resumes
Duration of the first glance
6–8 seconds: A recruiter typically spends about 6–8 seconds on an initial resume scan.
Source: Tufts Career Center
6–7 seconds on average: Employers look at resumes for 6–7 seconds on average.
Source: Indeed
Information consistency: An initial review takes 30 seconds, depending on resume clarity.
Source: StandOut CV
Extended review time
1–3 minutes: 57% of hiring managers spend 1–3 minutes reviewing resumes, while 21% spend over 3 minutes, and only 22% of hiring managers spend less than a minute.
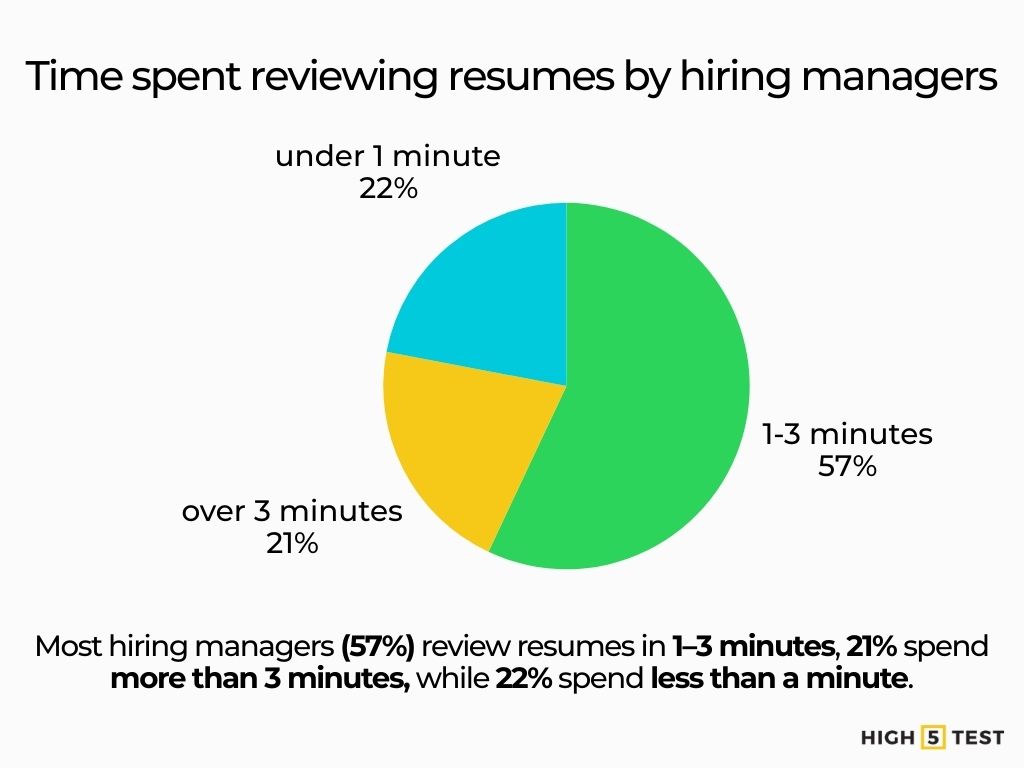
Source: Resume Genius
Additional comparison: Another survey found that 24% of hiring managers spend under 30 seconds on a resume.
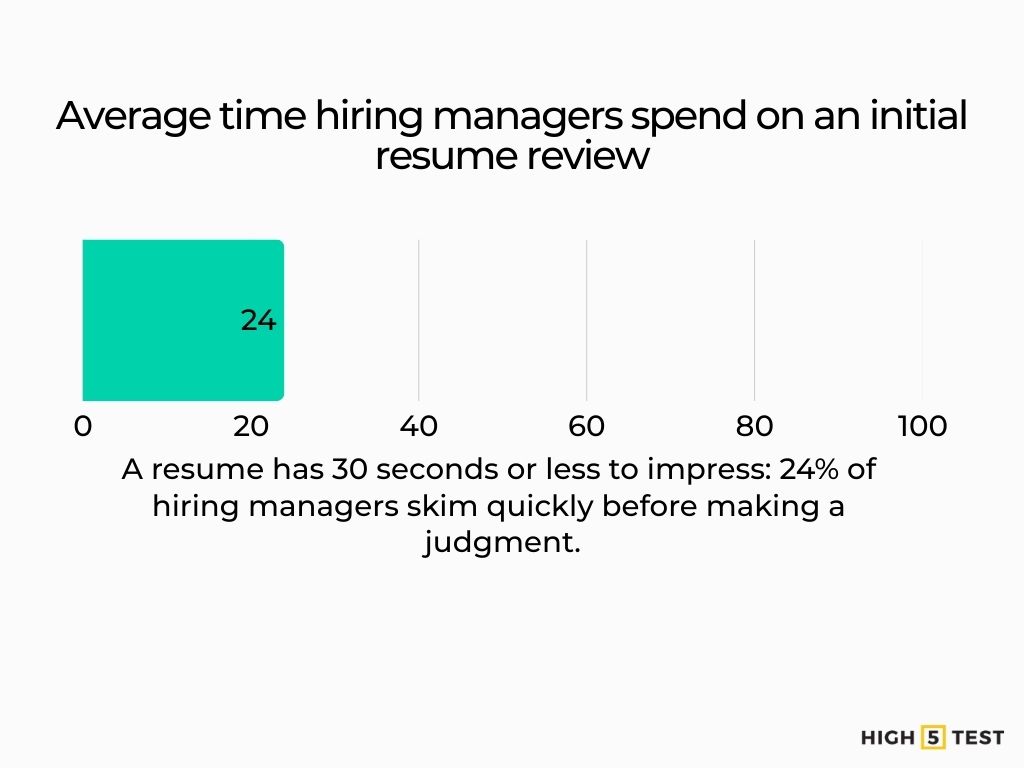
Source: CareerBuilder
Consequences of unquantified content
44% of hiring managers cite lack of measurable achievements as a resume dealbreaker.
Source: Resume Genius
40% higher chance: Resumes including hard metrics can have up to a 40% higher chance of securing an interview.
Source: Fast Company
Resume content insights (preferred sections)
Work experience
Less than 40% of employers reported that they are screening candidates by GPA. Employers increasingly value internships and major-related experience over GPA, shifting screening away from education.
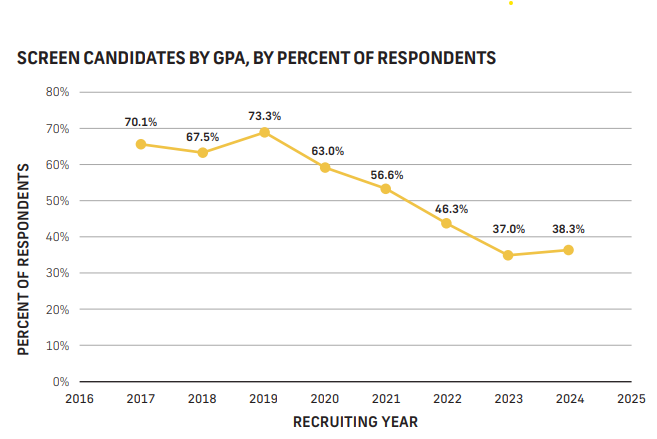
Source: NACE
Education
63% of hiring managers say education remains important; 47% are more likely to hire candidates with a higher GPA, and 75% want to see specific accomplishments in the education section.
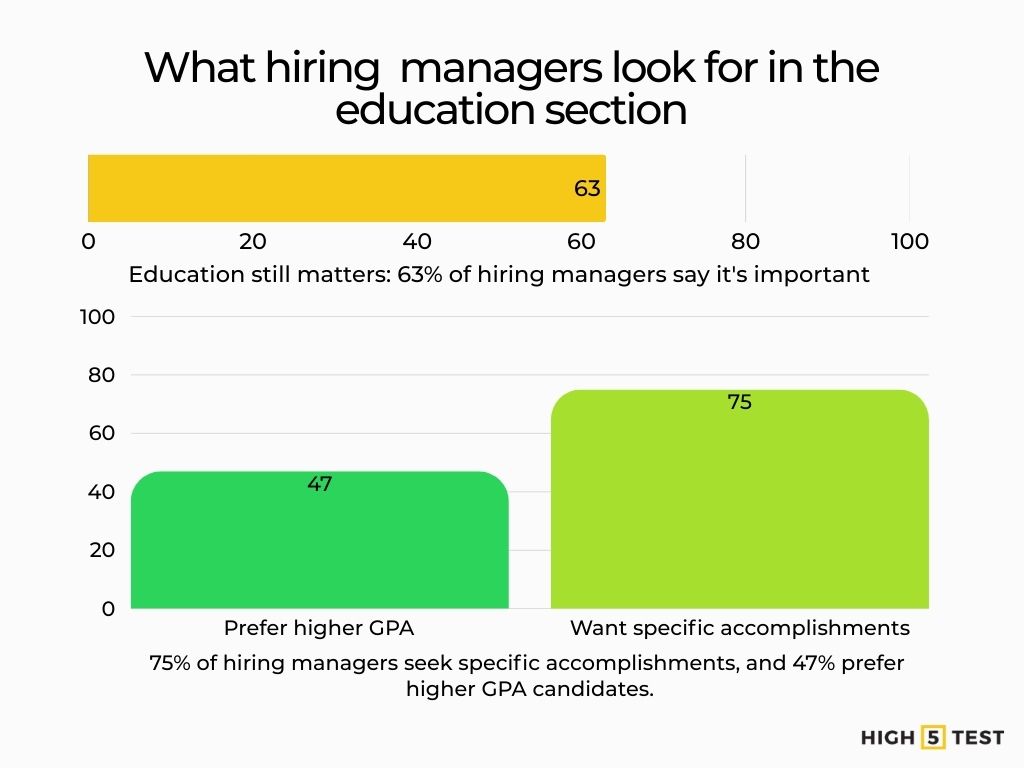
Source: Intelligent, NACE
Skills
Written communication, initiative, problem-solving, and teamwork are key: Nearly 88.3% of employers look for problem-solving evidence, 81% for teamwork; 70%+ value communication, initiative, and technical skills.
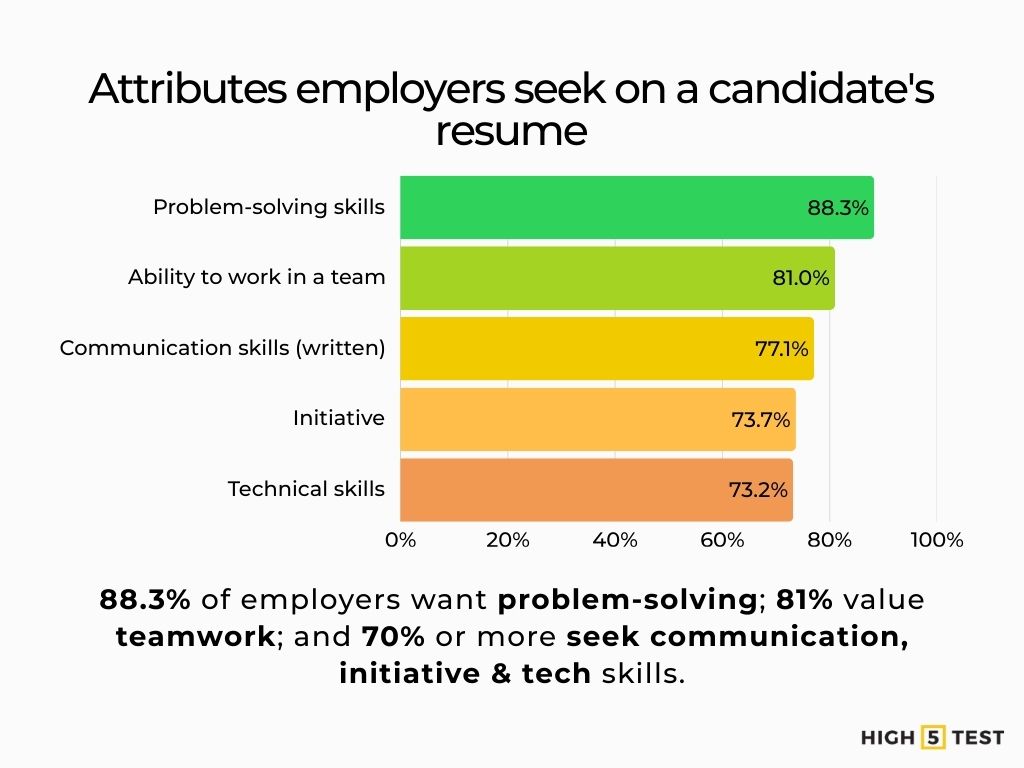
Source: NACE
AI skills: In 2025, 47% of hiring managers say AI abilities (like machine learning or generative AI) are among the top hard skills on a resume. Soft skills (problem-solving, communication, time management) also rank highly.
Source: ResumeBuilder
Customization and accomplishments
As noted, 75% of hiring managers want to see specific achievements, while 62% say a lack of customization is a standout mistake.
Source: Final Round AI, ResumeNow
Formatting preferences
73% of hiring managers reject candidates because of poorly formatted resumes.
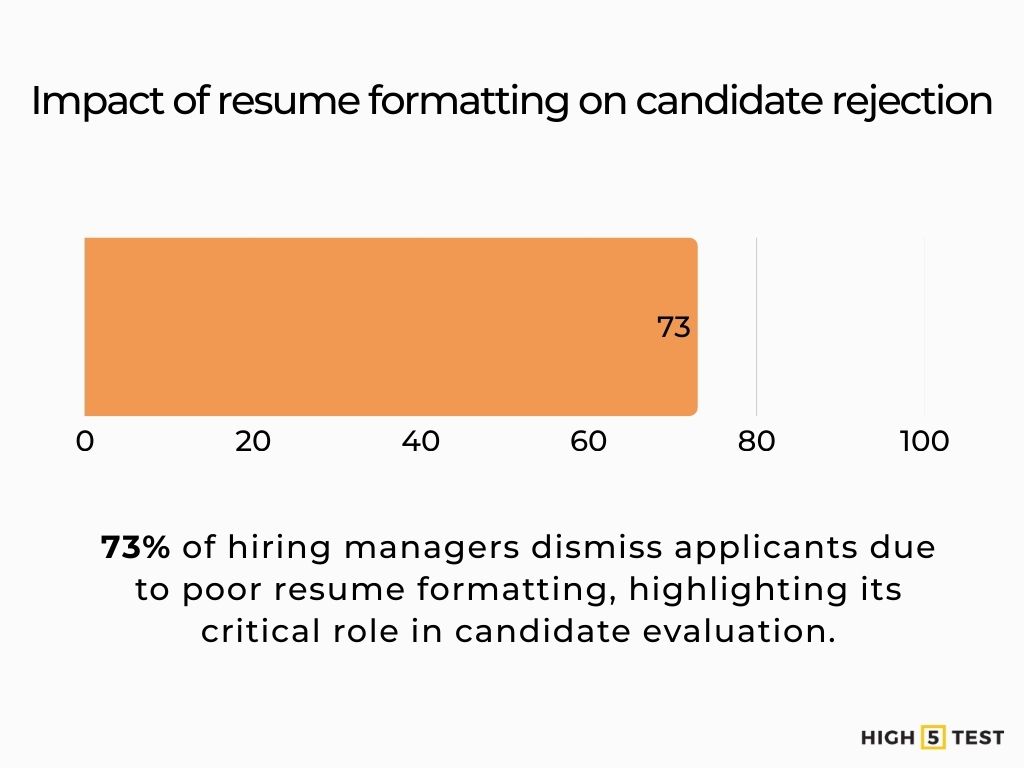
Source: Resume Templates
Length: A majority of 53% say that a resume should be two pages long, while 43% of hiring managers prefer one-page resumes.
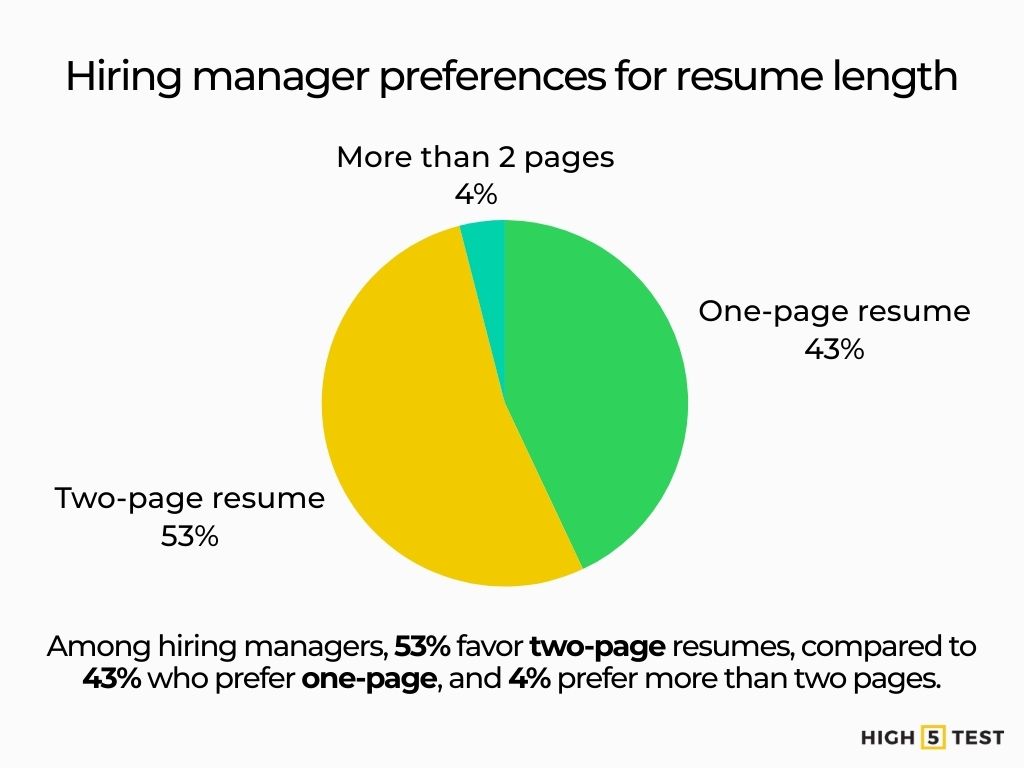
Source: Criteria
Press and practitioner guidance echo this: as AI screening favors complete, keyword-rich content, two pages can be advantageous for experienced candidates and remember to avoid fluff.
Source: Hiring Branch
Regional stats and market dynamics
Job competition by location
San Jose, CA, tops U.S. cities with 153.77 applicants per job ad (within one week).
Source: Resume.io
Competition is indeed rising across U.S. states, with the number of applicants per job rising from 7.5 to 40.9 (445.4%) year over year in Seattle.
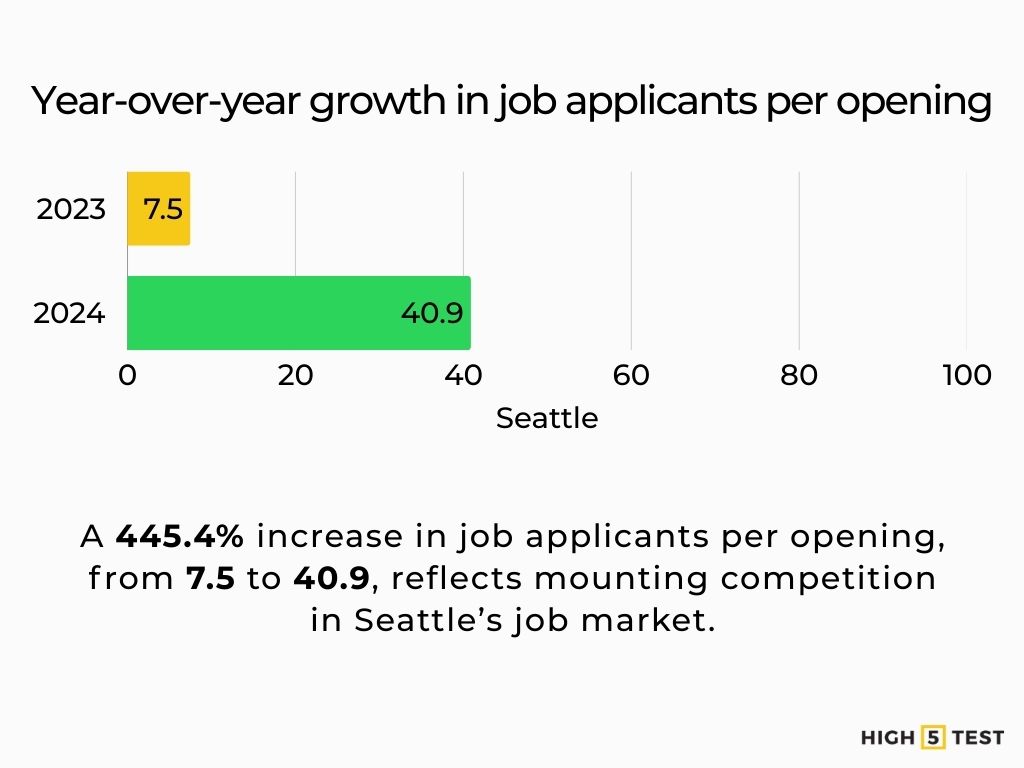
Source: Resume.io
Labor market conditions for new graduates
Job postings have dropped 15% for entry-level roles. Applications per job have surged 30%.
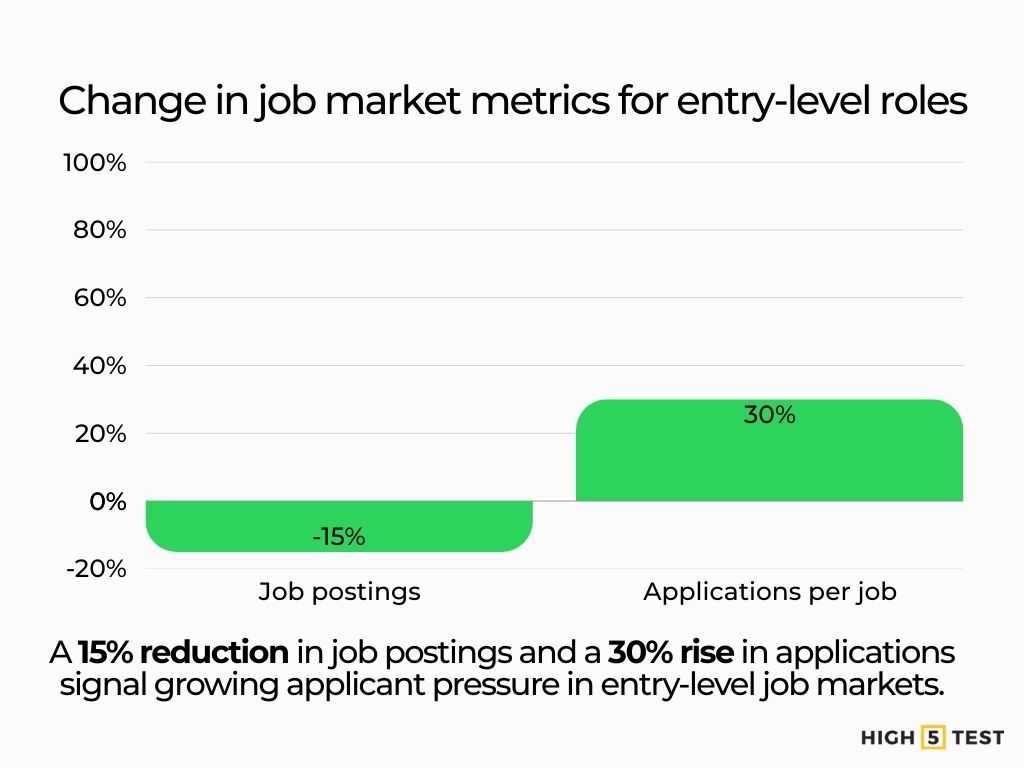
Source: Handshake
Hiring projections for new grads are up just 0.6%, revised down from earlier optimism.
Source: NACE
Job ads for new grads are down 15% July 2024–April 2025; initial hiring projections (+7.3%) fell to +0.6%. Graduate unemployment is now 4.8% (May 2025).
Source: Handshake, NACE, Federal Reserve Bank of New York
Strategic recommendations from resume stats & data
Emphasize quantifiable achievements (to avoid being discarded by 34%)
Recruiters repeatedly flag vague, “Miss America-style” claims; former Amazon recruiter Lindsay Mustain urges metrics to show impact.
Source: CNBC
64.8% of employers are using skills-based hiring practices, so it is advised to highlight evidence of job-ready skills and accomplishments, not just courses.
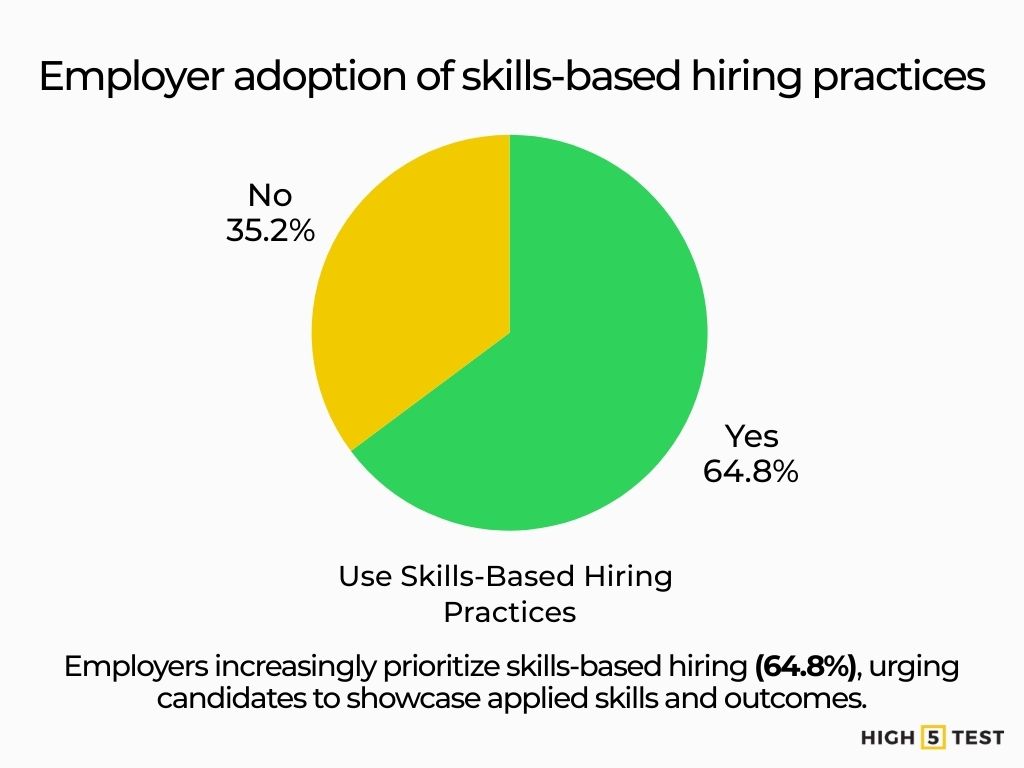
Source: NACE
Prioritize ATS optimization: keywords, simple formatting, structure
Most large U.S. employers run ATS. An audit shows 97.8% of Fortune 500 use an ATS; its recruiter survey reports 99.7% use ATS filters. Use exact job-description keywords and a clean layout.
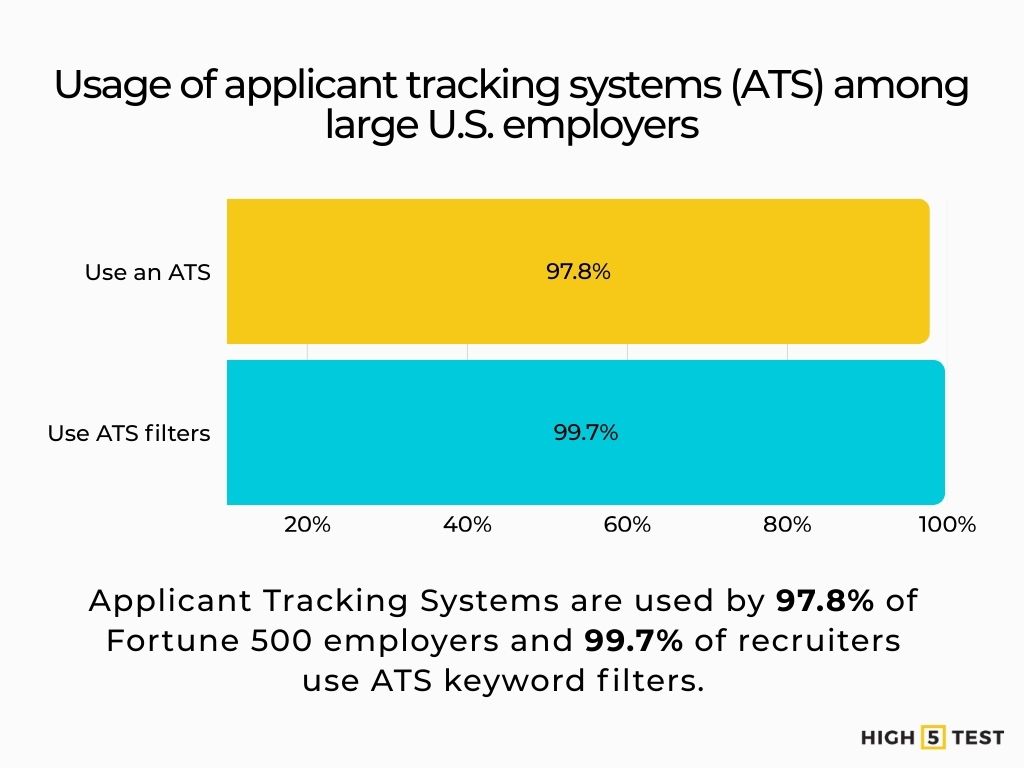
Source: Jobscan
Formatting rules that help parsing: avoid tables/columns/graphics; stick to standard section headers and one column.
Source: Jobscan
Keyword strategy: map role-specific phrases (skills, tools, titles) throughout the resume.
Source: Jobscan
Human first: AI can assist with keywords, but a clear, human-written resume still wins.
Source: City Personnel
Tailor per job and per location (reflecting local competition and signals)
Tailoring materially lifts interview odds: aligning your resume title with the job title increased interview rates ~3.5× in a 2024 analysis of 1M+ applications.
Source: Jobscan
Reflect local market conditions in what you emphasize. Example: A city/state LinkedIn analysis shows San Jose averages 107.6 applicants per ad (1 week)—a tougher filter than many markets; globally, Doha (Qatar) hits 399 applicants per ad. Tailoring proof-points and keywords to the region/industry helps you compete.
Source: Resume.io
When markets cool or heat up (e.g., 2024 San Jose ~153.77 vs. 2025 ~107.6), shift strategy—lean harder on referrals and niche boards in the most competitive metros.
Use writing & AI tools carefully
Improve clarity and readability, guard against bias
Adopt, but customize. In 2025, 83% of companies plan to use AI to review resumes; many U.S. hiring managers reject generic AI material (62% say uncustomized AI resumes are more likely to be rejected). Human-edit and personalize outputs.
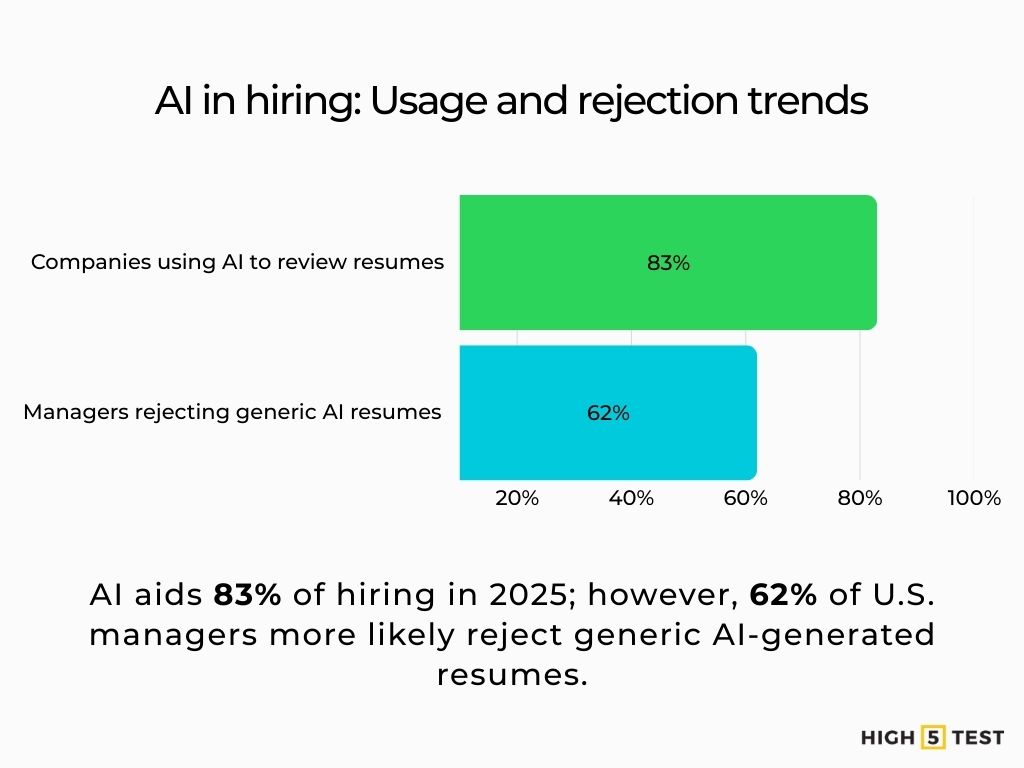
Source: Resume Builder, Resume Now
Bias is real. 2024–2025 studies show LLM-based screeners can exhibit race and gender name-based bias; use structured, job-related criteria, and keep human oversight in the loop.
Source: University of Washington Information School
Future resume and hiring trends, and predictions
Expect higher applications per role to persist in 2025; calibrate capacity (sourcing, screening, interviewer bandwidth) and prioritize job boards (60.6%) & custom sources (13.1%) channels, which over-index on hires vs. raw applicant volume in SMB benchmarks.
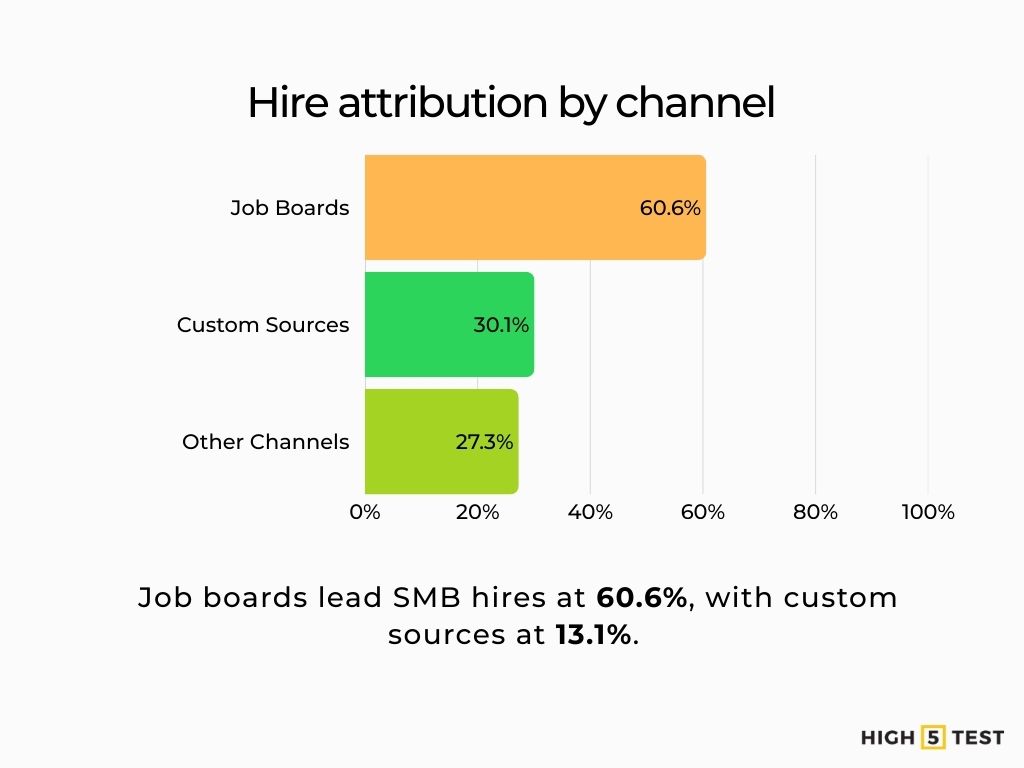
Source: CareerPlug
Mitigate screening bias (especially with AI tools) via structured, job-related criteria, adverse-impact monitoring, and transparent prompts/policies. Older candidates should age-proof resumes and foreground current, demonstrable skills.
Source: AARP
U.S. hiring pipelines are flooded with applications, with 2.6-3x growth in job applications, but few reach interviews; tailoring for relevance and ATS-readable structure remains essential.
Source: Ashby
Conclusion
Verified U.S. cases (notably Unilever) show large time and cost savings, reduced time-to-hire, and measurable gains in diversity when AI is used carefully. However, implementation matters greatly: tools must be transparent, biases must be audited, and recruiters still play a critical role in the final decision. The most successful organizations combine automated screening with human oversight, leadership assessment testing and invest in fairness, candidate experience, and clear communication. As hiring volumes and AI adoption continue to rise in 2025, those who ignore ethical or perceptual risks may pay the price in talent loss, legal exposure, or reputational damage.
