In the age of AI and big data, knowing yourself is more important than ever before, and the MBTI Personality Types is a great starting tool for better self-awareness. MBTI stands for Myers-Briggs Type IndicatorⓇ, and it was developed by Katharine Briggs and her daughter Isabel Myers. The personality model was heavily inspired by the work of Swiss psychoanalyst Carl Gustav Jung, although he never commented on the MBTI himself [1]. The first full MBTI manual was published in 1962, and 6 decades later, it exploded in popularity in the workplace. While understanding your MBTI personality type offers valuable self-awareness, uncovering your innate talents through a strengths-based approach like the HIGH5 assessment can be a game-changer. The HIGH5 goes a step further by scientifically measuring your realized strengths – a unique combination of talents, knowledge, and skills you’ve developed over time.
Maximize your potential by strategically applying your top strengths to roles, relationships, and goals optimally suited to your hard-wired abilities. In this guide, you’ll learn the 16 different MBTI personality types and how pairing this knowledge with your HIGH5 strengths can unlock new levels of self-actualization. We’ll explore what MBTI personality types are, and dive into the uniqueness of each type.
Note: The Myers-Briggs Type Indicator, along with its abbreviations Myers-Briggs and MBTI, are registered trademarks of The Myers & Briggs Foundation in the U.S. and other countries. HIGH5 is not associated with the organizations that produce or own the rights to the MBTI assessment.
Pro Tip From HIGH5
Before exploring the 16 MBTI personality types, take the HIGH5 strengths assessment to gain clarity on your unique talents and abilities. Reflect on how your top strengths, like analytical thinking or relationship building, complement your MBTI type’s traits. Look for ways your strengths could help you leverage or balance your personality preferences in different situations.
For example, if you’re an introvert with strong communication strengths, you can apply those talents in select social settings that energize you. Combining your HIGH5 strengths and MBTI knowledge allows you to amplify your self-awareness and strategically capitalize on your whole, multi-faceted self.
How does the MBTI test work?
The MBTI test contains a series of 94 questions that you answer to indicate your preference in various scenarios [2]. These answers are then analyzed to determine which of the 16 personality types best aligns with your natural inclinations and behaviors, revealing insights into how you perceive the world and make decisions. The assessment categorizes these preferences into four dimensions:
- Introversion/Extraversion (I/E)
- Sensing/Intuition (S/N)
- Thinking/Feeling (T/F)
- Judging/Perceiving (J/P)
Each dimension has two opposite poles, and your responses indicate where you fall on the spectrum for each. Let’s look at the 16 different types in greater detail, starting with the INFJ.
16 MBTI types explained in in-depth
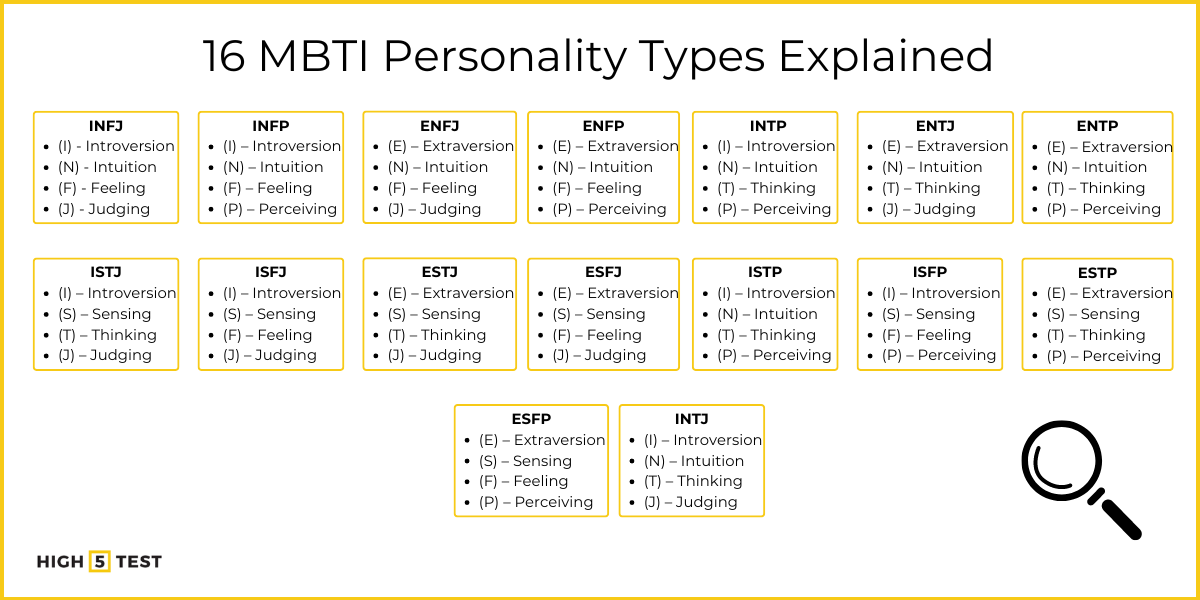
INFJ
(I) – Introversion, (N) – Intuition, (F) – Feeling, (J) – Judging
The INFJ personality type is called the “Advocate”. They’re creative and try to find a hidden meaning in everything and everyone that surrounds them. People with this personality type have high expectations for themselves and others. Because of that can be disappointed easily. A firm values help them to act in the world and develop a clear vision of their life. INFJs work deliberately towards implementing their ideals and can be both stubborn and sensitive in this pursuit.
INFP
(I) – Introversion, (N) – Intuition, (F) – Feeling, (P) – Perceiving
The INFP is also called the “Mediator”. They live according to their strong values and help to bring the best out of the people around them. Despite that, they are still flexible and can easily adapt to new situations, unless their dearly-held values are tested. INFPs are very loyal and value personal relationships, but are difficult to approach and become friends with.

ENFJ
(E) – Extraversion, (N) – Intuition, (F) – Feeling, (J) – Judging
The ENFJ is known as the “Giver,” because people with this personality type are always taking care of others, sometimes to their own detriment. They possibly possess the best “people skills” out of all personality types, are warm, compassionate, and love both, talking and listening. ENFJs are great partners and friends, but because of their great social skills, they can also be dangerous and manipulative, if their intentions are anything short of wholesome.
ENFP
(E) – Extraversion, (N) – Intuition, (F) – Feeling, (P) – Perceiving
The ENFP is called the “Champion”. ENFPs are extremely energetic, and enthusiastic and possess great emotional intelligence. They are flexible, love spontaneity, and dislike routine. Because of that, ENFPs flourish in environments where they are allowed to do what they want. One drawback of such energy and creativity is that they can be easily distracted and sometimes procrastinate on important tasks up until the very last moment.
ISTJ
(I) – Introversion, (S) – Sensing, (T) – Thinking, (J) – Judging
The ISTJ is also known as the “Inspector”. They are pragmatic, realistic, and responsible. Because of their high conscientiousness, they are dependable and you can trust them in both personal and working relationships. ISTJs are very detail-oriented and prefer logic and rationality over emotions, which can make them rather judgemental and insensitive. They don’t like new things and tend to put their trust in tradition.

ISFJ
(I) – Introversion, (S) – Sensing, (F) – Feeling, (J) – Judging
The ISFJ or the “Protector” is a personality type that is very detail-oriented and practical. Naturally, ISFJs enjoy routine in organized and harmonious environments, where everything goes according to plan. They are also sensitive and tend to negate their own emotions for the sake of other people. These characteristics make them great workers, but they are sometimes exploited in work environments.
ESTJ
(E) – Extraversion, (S) – Sensing, (T) – Thinking, (J) – Judging
The ESTJ is dubbed the “Director” because this personality type values tradition and rules, and are likely to hold other people accountable. It makes them great in civic and law-enforcement careers and ESTJs are great at leading and managing other people. However, the same characteristics that make them great at it, can cause problems in personal relationships. They can be too controlling and stubborn, following their own code of living and making everyone around them follow the same rules.
ESFJ
(E) – Extraversion, (S) – Sensing, (F) – Feeling, (J) – Judging
The ESFJ (known as the “Caregiver”) is outgoing and enjoys helping other people in need. This personality type is great at getting to know other people and understanding what makes them tick. ESFJs are great social organizers, as they are always up to schedule and organize social events. They are also a kind of social “sponge,” and absorb the energy of people surrounding them.

ISTP
(I) – Introversion, (N) – Intuition, (T) – Thinking, (P) – Perceiving
The ISTP is dubbed the “Crafter” because they enjoy new experiences and hands-on work. They are very crafty people; usually kinesthetically gifted, and possess a wide area of expertise. However, ISTPs get bored easily and tend to jump from one thing to another, which sometimes results in being a jack of all trades, yet a master of none.
ISFP
(I) – Introversion, (S) – Sensing, (F) – Feeling, (P) – Perceiving
The ISFP is alternatively known as the “Artist.” Just like popular culture depicts artists as reserved, creative and unique people, so are ISFPs. They tend to spend most of their time alone working on something they love. However, unlike most actual artists who enjoy dreaming about unique ideas, ISFPs tend to be more realistic and enjoy practical hands-on activities. Think pottery, woodcrafting, or painting.

ESTP
(E) – Extraversion, (S) – Sensing, (T) – Thinking, (P) – Perceiving
The ESTP is also called the “Persuader.” People with this personality type possess great people skills, are quick on their feet, and enjoy spontaneity. ESTPs hate planning things out, and prefer to just go with the flow and see how things turn out to be. Because they’re also impulsive and action-oriented, they are susceptible to easily avoidable mistakes. However, it also makes them fun people to be around, as their enthusiasm and spontaneity never get boring.
ESFP
(E) – Extraversion, (S) – Sensing, (F) – Feeling, (P) – Perceiving
The ESFP or the “Performer” is a personality type mostly characterized by its tendency to be the center of attention. They are natural at entertaining other people and have a strong desire to do so. Because of that, they are usually the class clowns or lives of the party, bringing everyone’s attention to their act. ESFPs are always looking for something new to do, and dislike routine and rules.
INTJ
(I) – Introversion, (N) – Intuition, (T) – Thinking, (J) – Judging
The INTJ is dubbed the “Architect,” because of their tendency to think big and have a vision for a better tomorrow. They have high expectations and prefer to indulge in abstract and theoretical concepts that can be honed to improve efficiency in the real world. INTJs are hard-working, and their grandiose ideas usually become implemented in reality at least to some degree. However, as they cannot fully fulfill their ideas in the real world, they usually get disappointed with the outcome of their work.
INTP
(I) – Introversion, (N) – Intuition, (T) – Thinking, (P) – Perceiving
The INTP personality type is called the “Thinker” because they love engaging in difficult and abstract ideas. INTPs usually prefer to just spend time reading and thinking about things, instead of socializing with people. That being said, INTPs value people who are close to them. They have a small, but tight-knitted circle of friends and are very loyal to it. INTPs are one of the best “out of the box” thinkers, but they also tend to overthink menial things and are plagued by self-doubt.

ENTJ
(E) – Extraversion, (N) – Intuition, (T) – Thinking, (J) – Judging
The ENTJ or the “Commander” is a personality type characterized by innate leadership qualities and assertiveness. ENTJs are great at organizing things and are good at making decisions. In case there’s a problem to solve, ENTJs will be the first in line to do so. That being said, they usually have a poor understanding of their own emotions. Despite that, ENTJs love being with other people and possess great social skills. Some of the drawbacks of ENTJs are that they are often stubborn, insensitive, and impatient.
ENTP
(E) – Extraversion, (N) – Intuition, (T) – Thinking, (P) – Perceiving
The ENTP is called the “Debater” because people with this personality type have great verbal ability and can communicate complex ideas with ease. ENTPs love talking to various people, and they usually turn simple and lighthearted conversations into heated debates. ENTPs love learning new things and studying the world around them. They are also creative, dislike routine, and enjoy freedom. They dislike it when someone tells them what to do. And so, the ENTP would rather go their own way.
MBTI personality type indicators explained
We’ve already briefly mentioned that each personality type consists of a combination of four dichotomous functions. In this section, we’re going to separately explain each component of personality types.
Extraversion (E) – Introversion (I)
This dichotomy shows how a person interacts with the outside world. Personality types with Extraversion cognitive function are most likely to enjoy spending time with other people and gain energy after socializing. Personality types with Introversion are more likely to spend time alone and prefer a smaller social circle. They tend to be slow, deliberate speakers and are less energetic, on the whole.
Sensing (S) – Intuition (N)
People with sensing prefer factual and pragmatic information over abstract ideas. They like to see the world in numbers and concrete figures. On the other hand, people with intuition like abstract ideas and theoretical concepts.

Thinking (T) – Feeling (F)
Thinking means an individual makes more rational decisions. They like to view their emotions through a lens of logic. They try to deal with emotions in a calculated way. People who have feeling function are more emotional, and compassionate, and can express their emotions more easily.
Judging (J) – Perceiving (P)
People with judges are conscientious. They enjoy order, harmony, and routine. Most commonly, they have their lives sorted out, and live in an organized routine. People who have perceiving, in contrast, prefer spontaneity over routine, like to have their options open, and can easily adapt to new situations.
What is the meaning of the letters in the MBTI assessment?
- E (Extraversion): Extraverts are energized by social interactions and tend to be more outwardly expressive and engaged with the external world.
- I (Introversion): Introverts derive energy from solitary activities and prefer deep, meaningful interactions with a smaller circle of friends rather than large social gatherings.
- S (Sensing): Sensing types focus on the present and concrete information gained from their senses; they are practical and detail-oriented.
- N (Intuition): Intuitives tend to focus on future possibilities and abstract theories; they value innovation over tradition.
- T (Thinking): Thinkers prioritize logic and objective criteria in their decision-making process and are often seen as direct and task-focused.
- F (Feeling): Feelers make decisions based on personal values and how outcomes will affect others, often showing empathy and compassion.
- J (Judging): Judging types prefer structure and firm decisions, and they value organized, planned, and controlled environments.
- P (Perceiving): Perceivers enjoy keeping their options open and like to be flexible and spontaneous, preferring a more laid-back approach to life.
Fun facts about MBTI personalities
- The MBTI types were developed by Katharine Briggs and Isabel Myers in the 1940s.
- The INFJ is the rarest MBTI personality type. According to the Myers-Briggs Foundation, only 1.5% of the US population has this personality type [3].
- According to the Myers-Briggs Foundation, the ISFJ is the most common MBTI personality type. 13.8% of people have this personality type [4].
- Some online surveys have shown that the ESFP is the most liked MBTI personality type.
MBTI types FAQ
What is the best MBTI personality type?
Every personality type has its unique strengths and areas for improvement. A great career for one may be a total nightmare for another. It’s tough to state which type is the best, although ENTJs, ESTJs, and ENTPs tend to earn the most, financially [5].
What are the 4 main MBTI types?
The four main MBTI types refer to the categories based on the primary sliding scales:
- Extraversion (E) vs. Introversion (I)
- Sensing (S) vs. Intuition (N)
- Thinking (T) vs. Feeling (F)
- Judging (J) vs. Perceiving (P)
Is the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator scientifically validated?
The Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) is widely used in various settings, including career counseling and team building, but it has received criticism for its lack of empirical support and scientific rigor.
While it offers valuable insights for personal growth and understanding interpersonal differences, it does not meet the standards typically required for clinical psychological assessments. Researchers often caution against using the MBTI for making critical decisions as it lacks predictive reliability and validity [6].
Overall Conclusion
Knowing your type can allow you to understand your strengths and weaknesses, improve personal relationships, and accelerate your career. Knowing which type of the 16 you are can give you valuable insights into your preferences. Combine this with your top five strengths from HIGH5, and you’re well on your way to career success!
References:
- Myers S. (2016). Myers-Briggs typology and Jungian individuation. The Journal of analytical psychology, 61(3), 289–308. https://doi.org/10.1111/1468-5922.12233.
- McDermott, N. (2024, January 5). Myers-Briggs Type Indicator: What To Know About This Popular Personality Test. Forbes. https://www.forbes.com/health/mind/myers-briggs-personality-test.
- 5 Rare Personality Types. (2023, August 26). Psych Central. https://psychcentral.com/health/rarest-personality-type#infj.
- What is the most common personality type? (With definitions). (2024). Indeed Career Guide. https://uk.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/most-common-personality-type.
- Ross, J. (2021, October 21). How does your personality type affect your income?. World Economic Forum. https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2021/10/personality-type-earning-wages.
- Zárate-Torres, R., & Correa, J. C. (2023). How good is the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator for predicting leadership-related behaviors?. Frontiers in psychology, 14, 940961. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.940961.


